minikube kubeconfig
- from .kube/config file, extract cluster.certificate-authority-data| base64 -d > ca.crt
openssl x509 -in ca.crt -text -noout > ca.crt.decode
From ca.crt.decode:
Issuer: CN = minikubeCA
Subject: CN = minikubeCA
- from .kube/config file, extract user.user. client-certificate-data | base64 -d > client.crt
openssl x509 -in client.crt -text -noout >
client.crt.decode
From client.crt.decode
Issuer: CN = minikubeCA
Subject: O = system:masters, CN = kubernetes-admin
CKS Tips
1. Shortcut
export now="--force --grace-period 0" # k delete pod x $now
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: mypod
spec:
containers:
- name: mypod
image: redis
volumeMounts:
- name: foo
mountPath: "/etc/foo"
readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: foo
secret:
secretName: mysecret
10. securityContext.capabilities is only for container, not for pod
11. securityContext.readOnlyRootFilesystem is only for container, not for pod. Here we should use word "Root" and s is small in system.
12. Instead of applying (1) label to node and (2) then use nodeSelector, we can use nodeName in pod spec.
spec:
nodeName: cluster1-worker2 # add
13. To run command inside pod and take its output to outside pod. here the final command to be run inside the pod should be at the end.
14. To run etcdctl
ETCDCTL_API=3
cat /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-apiserver.yaml | grep etcd
14.3. Now do mapping. parameter value in kube-apiserver.yaml to input argument for etcd
--etcd-certfile mapped to --cert
--etcd-keyfile mapped to --key
system:serviceaccount:(singular) is the prefix for service account usernames.system:serviceaccounts:(plural) is the prefix for service account groups.
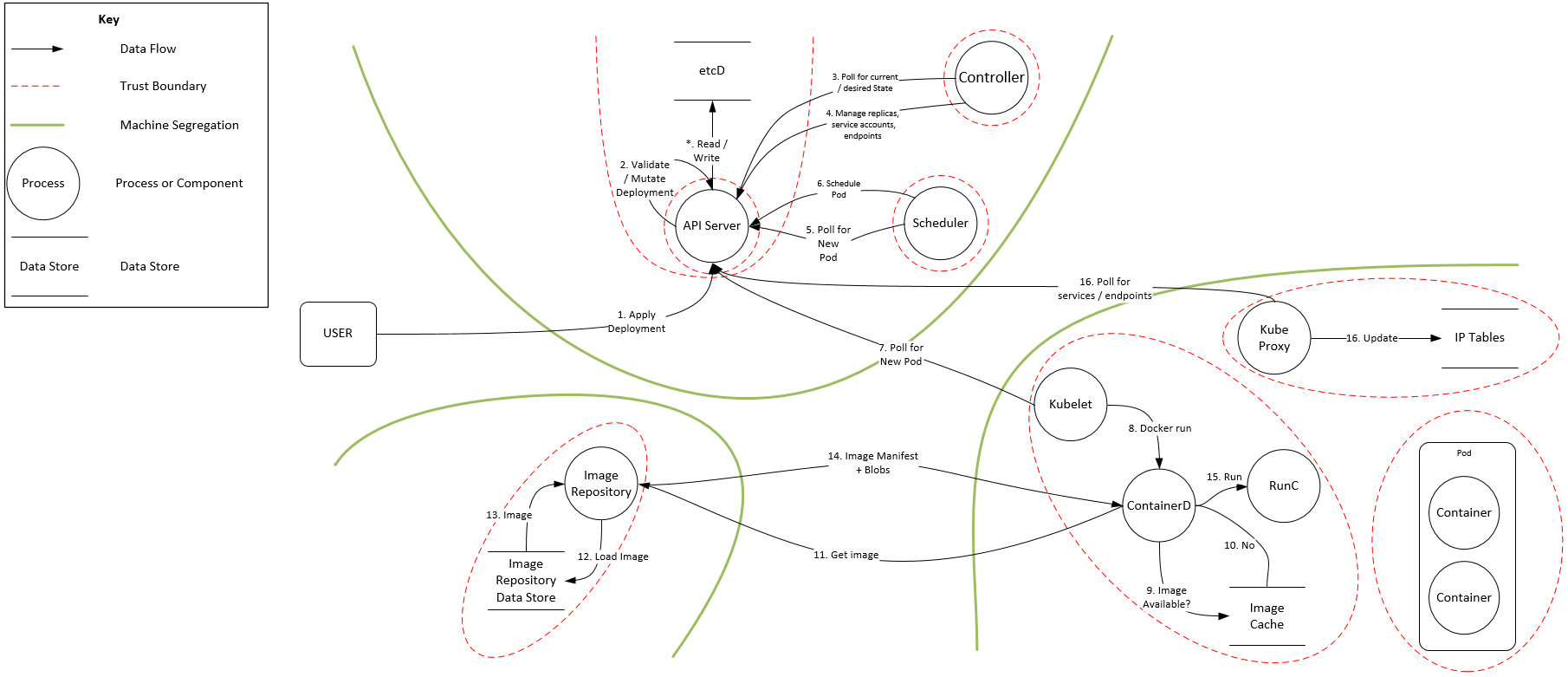
K8s. Flow
Security Context and PSP
Security Context
Only for container
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false . It is for setuid and setgid
allowPrivilegeEscalation:
if (CAP_SYS_ADMIN || Privileged mode) then AllowPrivilegeEscalation = SSeue
=============
capabilities:
drop:
- all
add: ["MKNOD"]
in PSP we have
allowedCapabilities:
- '*'
requiredDropCapabilities:
- ALL
=============
privileged: true avoid it.
=============
procMount: true is for nested container useful for in-cluster build process
=============
readOnlyRootFilesystem: true for immutable container
=============
For container and pod both
container settings will get precedence.
=============
runAsUser and runAsGroup are runtime configuration. If not defined then UID as per data in image
If runAsNonRoot = True then image should have UID. Same UID should be in host.
=============
securityContext:
level: "s0:c123,c456"
we can specify level, role, type, user. They are labels for file, process and ports. They are collectively called called "context" in SELinux terms.
=============
type = Localhost | Unconfined | RuntimeDefault
type: Localhost
localhostProfile: profiles/name.json
where kuelet-root-dir = /var/lib/kubelet .
It is configured with seccomp-profile-root flag for kubelet. This flag is deprecited since 1.19 . If seccomp-profile-root flag is not defined, the default path will be used, which is <root-dir>/seccomp where <root-dir> is specified by the --root-dir flag.
* type: RuntimeDefault means same seccomp profile as container runtime default is applied
* type: Localhost, then only, we need to set localhostProfile
We need to use annotation (optional)
seccomp.security.alpha.kubernetes.io/pod: localhost/profiles/audit.json
Path for seccomp profiles: https://k8s.io/examples/pods/security/seccomp/profiles/
=============
Only for Pod
fsGroup
the permission bit will be | with rw-rw----
ownership and permission change recursively for all content in mounted volume as per fsGroup
=============
fsGroupChangePolicy = OnRootMismatch | Always
no impact on emptyDir, secret and configMap
OnRootMismatch: It will save time. The permission and ownership only change if root level folder has mismatch with expected fsGroup.
If DelegateFSGroupToCSIDriver feature gate is enabled then this is done by CSI driver. CSI driver will not respect fsGroupChangePolicy
=============
supplementalGroups
A list of groups applied to the first process run in each container, in addition to the container's primary GID.
=============
sysctls
====================================================
Here Discretionary Access Control (DAC) is related fields are: runAsUser, runAsGroup, runAsNonRoot, readOnlyRootFilesystem
Here volume related fields are: fsGroup and seLinuxOptions. We set only level at seLinuxOptions and as per level, labels applies to all containers and volumes.
PodSecurityPolicy
Pod's scrutiny attributes. Defined at cluster level. It controls security sensitive aspects of the pod specification. It define a set of conditions that a pod must run with in order to be accepted into the system, as well as defaults for the related fields.
It (1) restrict pod creation (2) restrict pod update (3) provide default value
=============
- "privileged" container (Privileged Mode). It is part of PSP. But it control container level "security context"
=============
- host-level ns (network, PID, IPC) "hostPID", "hostIPC", "hostNetwork". If hostPID allowed then container can escalate privilege using ptrace system call.
=============
- host ports "hostPorts"
- min: 0
max: 65535
- different types of volumes. E.g. "allowedFlexVolumes" "volumes"
=============
- host's filesystem E.g. "fsGroup"
fsGroup = MustRunAs | MayRunAs | RunAsAny
We shall specify 1+ range if fsGroup = MustRunAs | MayRunAs. In case of MustRunAs the fsGroup at Pod Security Context is set as min value. in case of MayRunAs, the default value for fsGroup at Pod Security Context, is unset
=============
- RO root filesystem for containers (DAC) "readOnlyRootFilesystem"
=============
- user IDs and group IDs (DAC) "runAsUser" "runAsGroup" "supplementalGroups"
runAsUser = MustRunAs | MustRunAsNonRoot | RunAsAny
runAsGroup = MustRunAs | MayRunAs | RunAsAny
supplementalGroups = MustRunAs | MayRunAs | RunAsAny
=============
- containers' privilege escalation "allowPrivilegeEscalation" "defaultAllowPrivilegeEscalation". Here defaultAllowPrivilegeEscalation, set values for allowPrivilegeEscalation, if not set.
=============
- containers' Linux capabilities (Linux Capabilities): "defaultAddCapabilities", "requiredDropCapabilities", "allowedCapabilities"
=============
- SELinux "seLinux"
RunAsAny means: Apparmor is used instead of SELinux.
=============
- seccomp and AppArmor profiles : using annotations.
seccomp.security.alpha.kubernetes.io/allowedProfileNames
apparmor.security.beta.kubernetes.io/defaultProfileName
If this annotation is not specified then default seccomp cannot be changed
=============
- sysctls that a pod can run: "forbiddenSysctls", "allowedUnsafeSysctls"
=============
- a proc mount type to be used. "allowedProcMountTypes" and "DefaultProcMount"
allowedHostPaths:
# This allows "/foo", "/foo/", "/foo/bar" etc., but
# disallows "/fool", "/etc/foo" etc.
# "/foo/../" is never valid.
- pathPrefix: "/foo"
readOnly: true # only allow read-only mounts
=============
PSP Policy Order
1. non-mutating policy in any order
2. mutating policy in alphabetical order of name
Good Reference:
A Good article: https://www.linux.com/training-tutorials/overview-linux-kernel-security-features/
Abbreviation
ASLR Address Space Layout Randomization
DAC Discretionary Access Control
IMA Integrity Measurement Architecture
MAC Mandatory Access Control
PAM Pluggable Authentication Modules
7. Workload Considerations : Falco
Falco by Sysdig: multiple components (user space program, configuration, driver) working together in order to evaluate system calls against rules, and generate alerts when a rule is broken:
rule has lists. rule can have reference to list. List can be part of macro and other list, in addition to part of rule.
rule has 5 k-v pairs. (1) name, (2) description , (3) condition : Filtering expression for events. (4) output, (5) priority. (emergency, alert, critical, error, warning, notice, informational, debug)
rule has 4 optional K-v pairs.(1) enabled. default is true (2) tags (filesystem, software_mgmt, process, database, host, shell, container, cis, users, network) . -T option to disable rules with given tag. -t option to enable. (3) warn_evttypes default is true. (4) skip-if-unknown-filter default is false. 5th one added (5) exceptions : a set of conditions that cause the rule to not generate an alert.
- Falco comes with many rules in /etc/falco/falco_rules.yaml file. They can be overwritten by /etc/falco/falco_rules.local.yaml file. E.g. to disable rule : We can add rule with same name and "append: true" + "enabled: false"
- evt.dir = < indicates end of system call and evt.dir = > indicates beginning of system call. dir = direction
- We have K8s related context: k8s.[pod | rc | svc | rs | deployment].[name | id \ label | labels] + many fields from K8s audit logs.
with macro part of rule can be re-used. There are many default macros.
Falco runs with K8s-audit on. So we need to specify audit policy file at API server argument --audit-policy-file
We can configure webhook in API server with this arguement
--audit-webhook-config-file=/etc/kubernetes/audit-webhook-kubeconfig
This YAML file shall define Config kind.
We can see Falco output with journalctl command.
Reference :
https://github.com/falcosecurity/falco/blob/master/rules/k8s_audit_rules.yaml
https://v1-17.docs.kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/debug-application-cluster/falco/